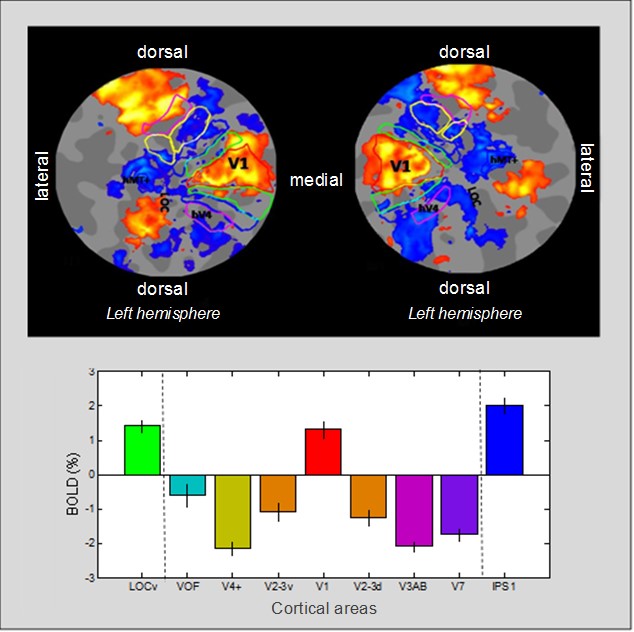
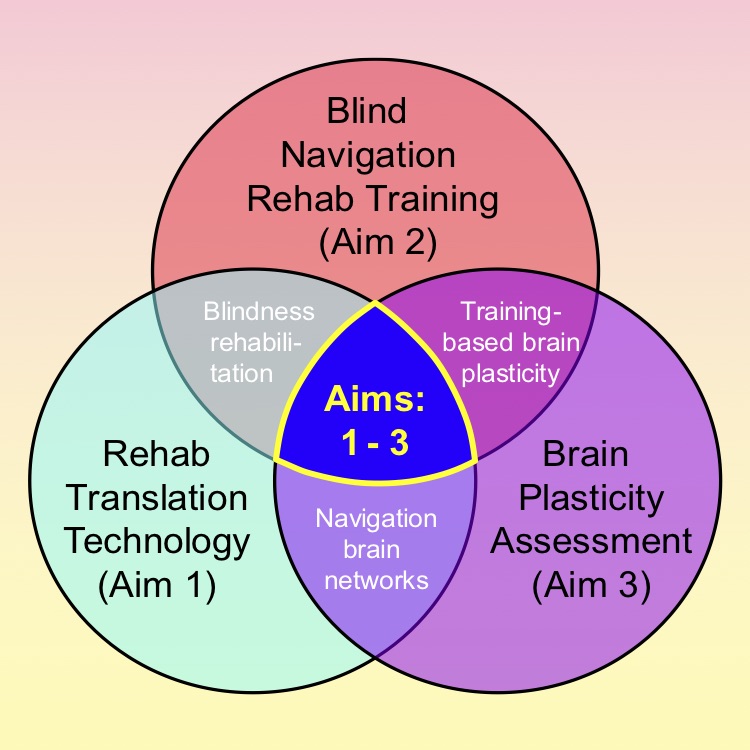
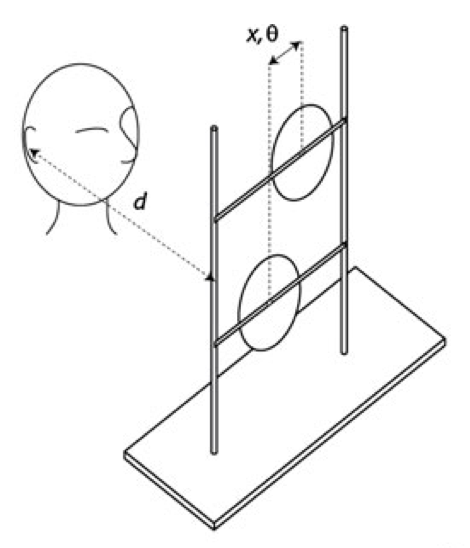
Cerebral Visual Impairment (CVI): An in-depth study of visual functioning in everyday life
The purpose of this research study is to learn about how cerebral visual impairment affects everyday visually guided behaviours and determine interventions to treat the difficulties. This study is conducted remotely through telephone or video link and also in person at the laboratory.